-
Windows
 Windows
Windows
-
French Doors
 French Doors
French Doors
-
Patio Doors
 Patio Doors
Patio Doors
-
Front Doors
 Front Doors
Front Doors
-
Roller Shutters
 Roller Shutters
Roller Shutters
-
Window Sills
 Window Sills
Window Sills
-
Sign in
Contact us
Expert Ioannis Marsellos, 12. November 2024
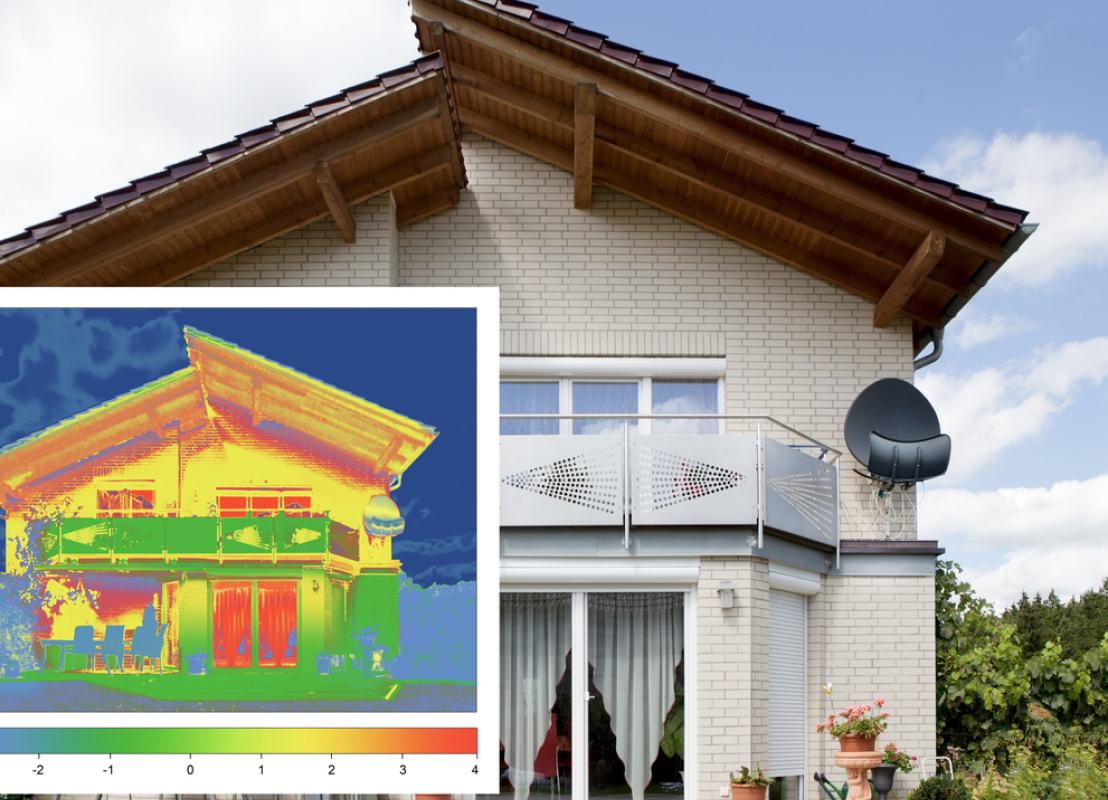

U-values are a way of measuring the energy performance of different building components. A u-value, also known as a heat transfer coefficient, defines the amount of heat transferred through a window, door, or wall, for example, each hour per square metre. The value is measured in W/m²K and the lower the value, the more energy-efficient the product because less heat transmission or energy loss occurs.
As an example, for one of our most insulating windows, the uPVC Kömmerling 88 MD model with an impressively low u-value measure of 0.73 W/m²K, relatively few watts of energy are transmitted per square metre for each degree of temperature difference between the window's interior and exterior.
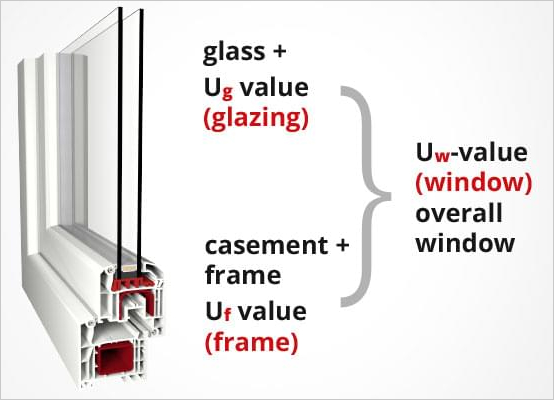
The overall u-value, the "Uw", of one of our windows or French doors comes from the values of its glazing, the "Ug", and of its frame, the "Uf". It is normal for the Ug, the u-value measure for the glass, to be lower than that of the frame.
This is because quality glazing is a more insulating material that will result in less heat loss or energy transfer between inside and outside. This also means that larger windows or those with more glazing along with modern purpose-designed frames tend to be the best insulators with the lowest thermal transmittance.
Quality, professional products, such as those from windows24.com, can make a big difference when it comes to insulation for windows and doors. To the right is a list of the key building components that can influence the u-value and thermal performance of products:
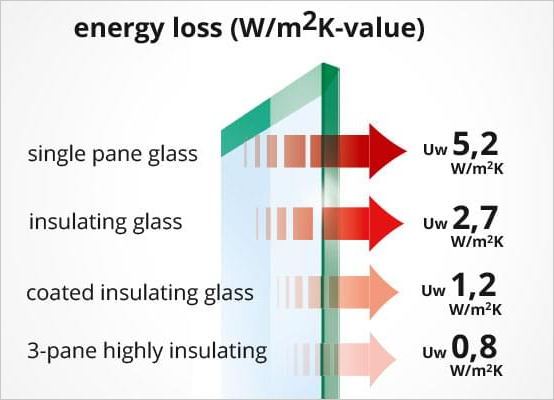
When it comes to the type of glass, the more panes the better. Triple-glazed or "triple-pane" highly insulating windows, featuring three panes of glass, for example, result in less energy loss because heat conduction is reduced due to their thickness.
When the space between panes, such as in insulating glass, are filled with inert noble gases like Argon that are denser and have a lower thermal conductivity than air, the u-value is also reduced.
Low-e coatings are then also available for the glazing's surface, which help to maintain a comfortable and stable interior temperature by reflecting excess external heat from solar radiation.
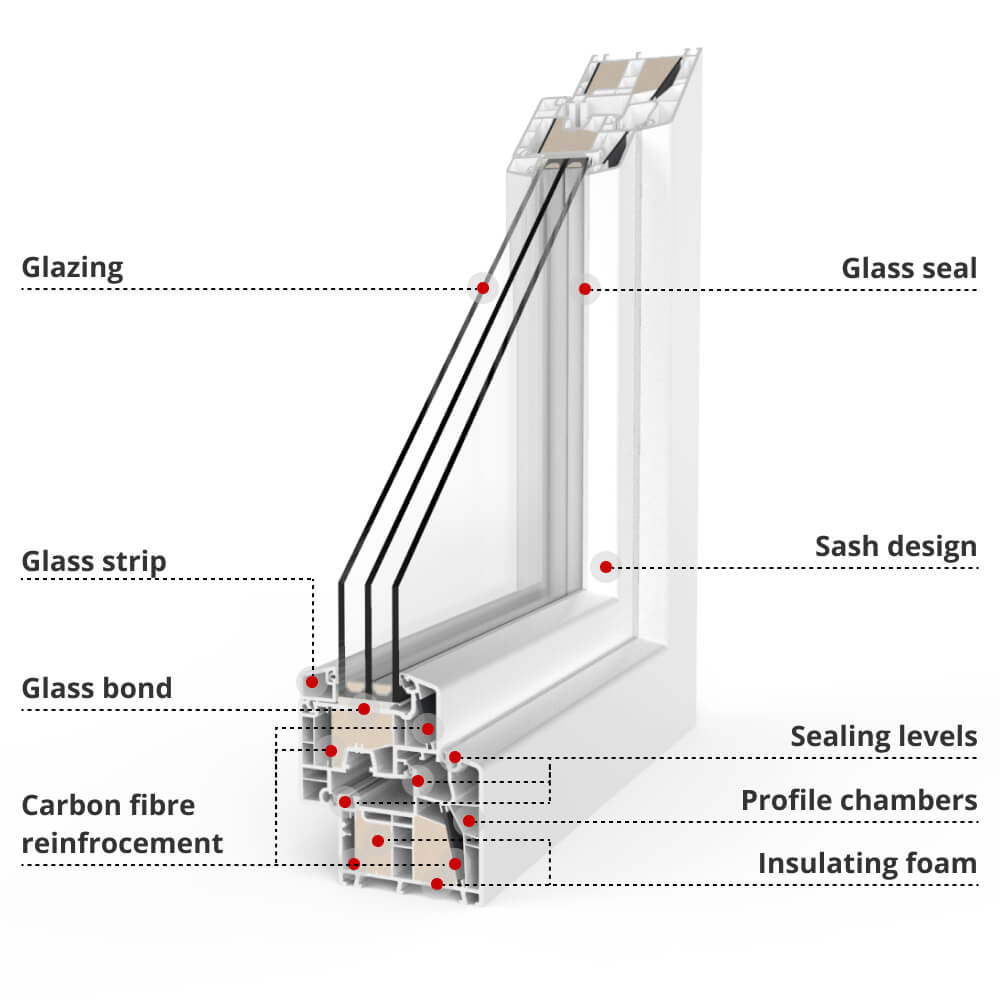
Quality thermal windows and French doors consist of more than a solid piece of frame. uPVC windows, those with the best insulation, are innovatively designed with specific features.
Multiple air-trapping chambers inside the frame and sash act as a thermal break. This prevents heat from being conducted and lost through the window or French door.
Some particularly modern models, such as aluplast's energeto 8000ED profile then also feature an integrated insulating foam material and carbon fibre reinforcement as well as multiple seals to further improve thermal performance.
Although the initial purchase cost may be slightly higher than that of a standard product, opting for an energy-saving window or French door pays off in terms of savings long-term and excellent durability. With less heat lost, money can be saved on winter bills, for example. In summer, because overall energy transmission via conduction through the product is minimised, undesirable heat from outside is also prevented from largely effecting interior temperatures.
This makes for a comfortable and energy efficient indoor climate that saves on cooling systems while reducing carbon footprint. Many modern thermal windows, such as those from windows24.com , then also come with a 5 or 10-year warranty thanks to their particularly long product life and are certified to meet regulations.
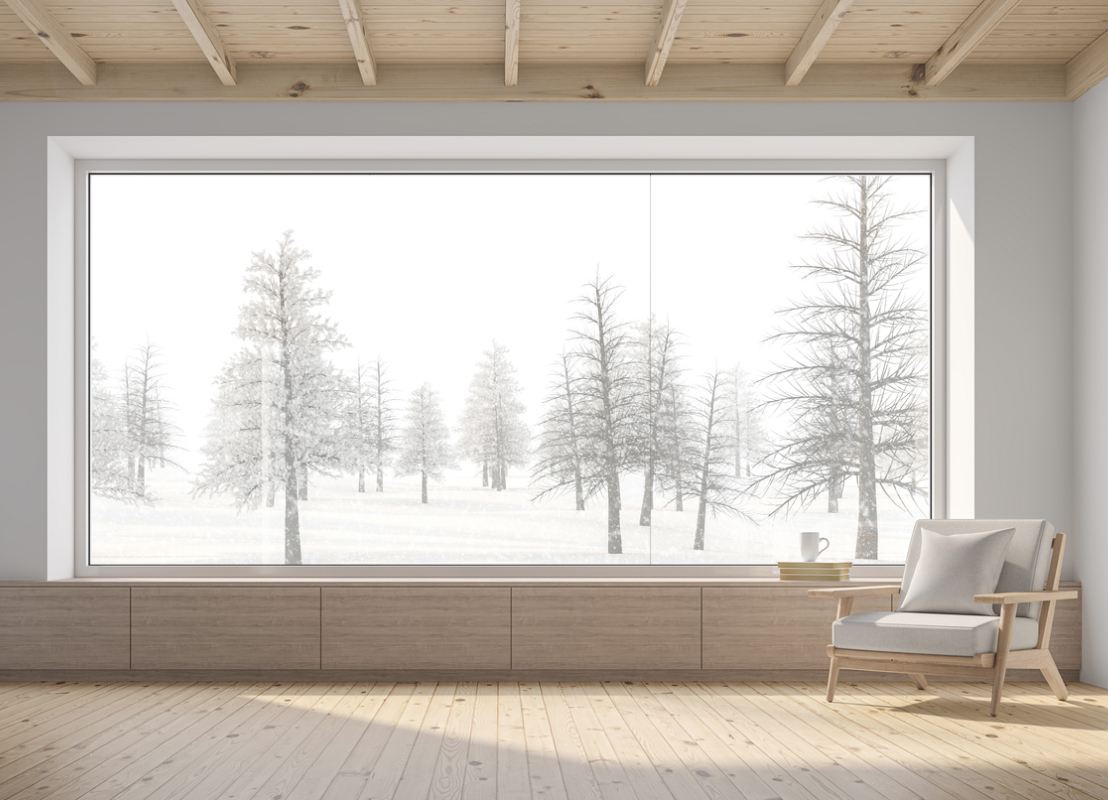

Windows and doors with good u-values and insulation can have buildings meet high sustainability standards. Our profiles, such as the wood-alu Eco Idealu Classicline model, have met the German Passive House Institute's requirements of having a Uw value of under 0.8 W/(m²K) and being able to maintain a steady indoor temperature that does not exceed 25 °C for more than 10% of hours annually, for example. Such passive house profiles can save up to 90% on regular energy usage.
In terms of other certificates and regulations, in some countries, such as the UK, governments are increasingly publishing energy-related building documentation. The 2023 Approved Document L, for example, states that replacement windows can't have a worse u-value than those they replace and set 1.4 W/(m²K) as the minimum. For new-builds, where windows have more than 60% of the internal face glazed, this figure can be as low as 1.2 W/(m²K).