-
Windows
 Windows
Windows
-
French Doors
 French Doors
French Doors
-
Patio Doors
 Patio Doors
Patio Doors
-
Front Doors
 Front Doors
Front Doors
-
Roller Shutters
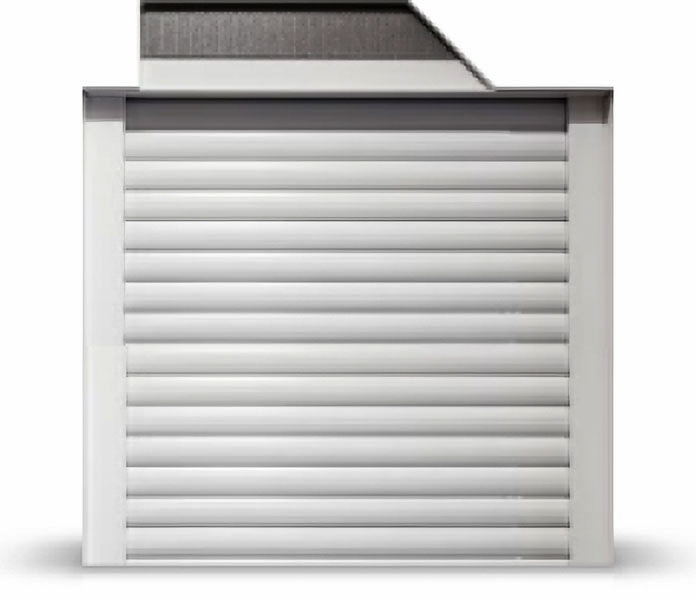 Roller Shutters
Roller Shutters
-
Window Sills
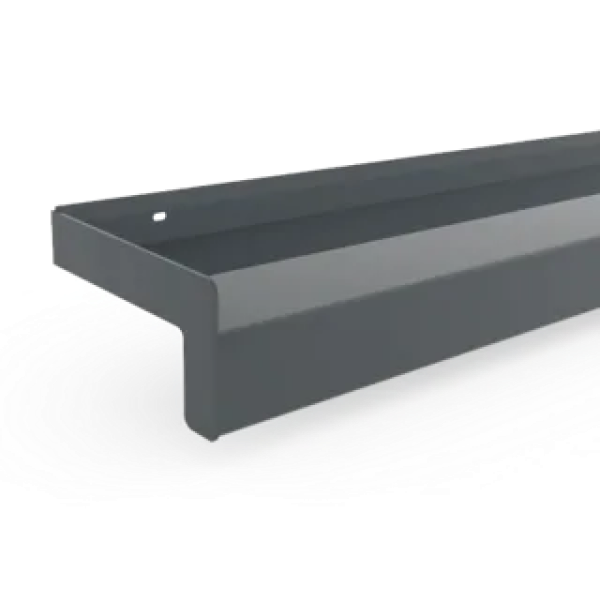 Window Sills
Window Sills
-
Sign in
Contact us

Nowadays, it is would be nearly impossible to find a building made without glass. Glazing, as used in the fenestration industry, is the part of a window made of glass, differentiating it from the window's frame, or profile. Common types of glazing used in building applications include clear and tinted float glass, tempered glass, and laminated glass as well as a variety of coated glasses, offered in single or double glazing. Glazing can be mounted on the surface of a window sash or door stile, usually made of wood, aluminum or vinyl (uPVC). The glass is fixed into a rabbet in the frame. Whether building a private home, office or large building, the choice of glazing plays a large role in the building's overall energy efficiency, security and noise levels.
In modern window manufacturing and mounting, only multi-layered insulating glass is used, meaning two or more panes are bonded above spacers with putty. The insulating glass is surrounded by a secondary seal to create laminated insulating glass edge. The separate glass panes usually have a thickness of 4mm, but they can also have 5, 6 or 8mm depending on their size and function (such as noise insulation glass). The larger they get, the thicker they have to be made due to static. Special glazing is available independently of the window material, being available for aluminum, wood and vinyl frames.
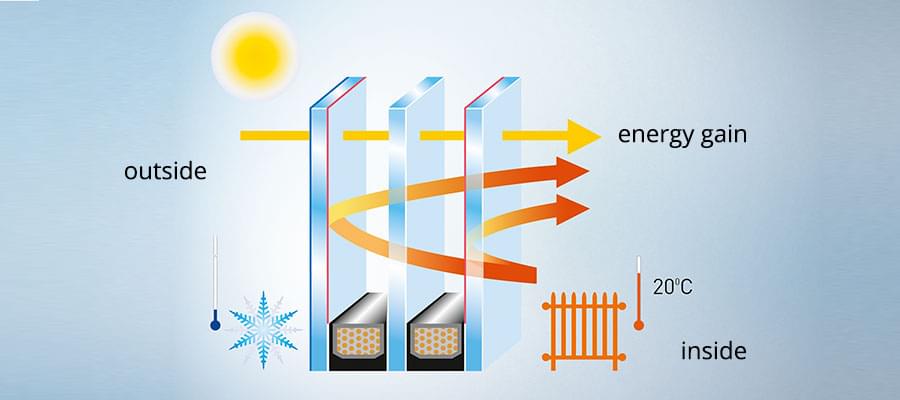
High-quality insulating glazing reduces energy costs from heating. Thanks to the higher surface temperature and improved joint impermeability, air inside the room doesn’t cool down saving energy, heat and costs. Additional solar protection can also be added as required.
Safety glazing can reduce many potential hazards such as injury, falling or burglary. There are two main types of safety glass: single glazing safety glass (toughened/tempered) and laminated safety glass.
In single pane safety glass, the stability under tension is increased so as to better resist temperature fluctuations and cracks. If broken, it breaks into tiny pieces with many pieces still hanging together to reduce potential injury, especially from sharp edges. Single pane safety glass is often used in vehicles for example, in the side and rear windows. In home windows, it reduces the possibility of stress fractures occurring and risk of injury.
When employing laminated safety glass there are at least two panes of float glass, which are coated with layers of tear proof 0.38 mm thick polyvinyl butyral (PVB) foil. Under pressure and at high temperatures - after laying the panes on top of each other together with the foil - the two materials are pressed together and then finally molded together under the heat of an autoclave.
Also known as ornamental glass, it is given its characteristic surface structure via a special rolling technique. This helps reduce visibility but not light transmission which is ideal for interior places requiring both light and privacy, such as bathrooms. Its decorative appearance makes this a popular choice for doors, windows and facades. However, ornamental glass can break more easily meaning a fine mesh wire is generally incorporated to boost its toughness. Nevertheless, wire-reinforced glass is more liable to break than float glass and therefore not suitable for use as safety glass.

Acoustic insulation entails thicker panes designed to substantially reduce outside noise. For sound reduction, the entire window's performance has to be evaluated, including the frame, not just the glazing itself. Homeowners in busy areas will hear a noticeable improvement in outside noise by replacing old windows.

Solar control glass is used in order to avoid and minimize extreme increases in the indoor temperatures. The glass panes are treated with a reflective coating or an absorbant, colored layer (iron oxide or copper oxide). The advantages of solar glazing include:
